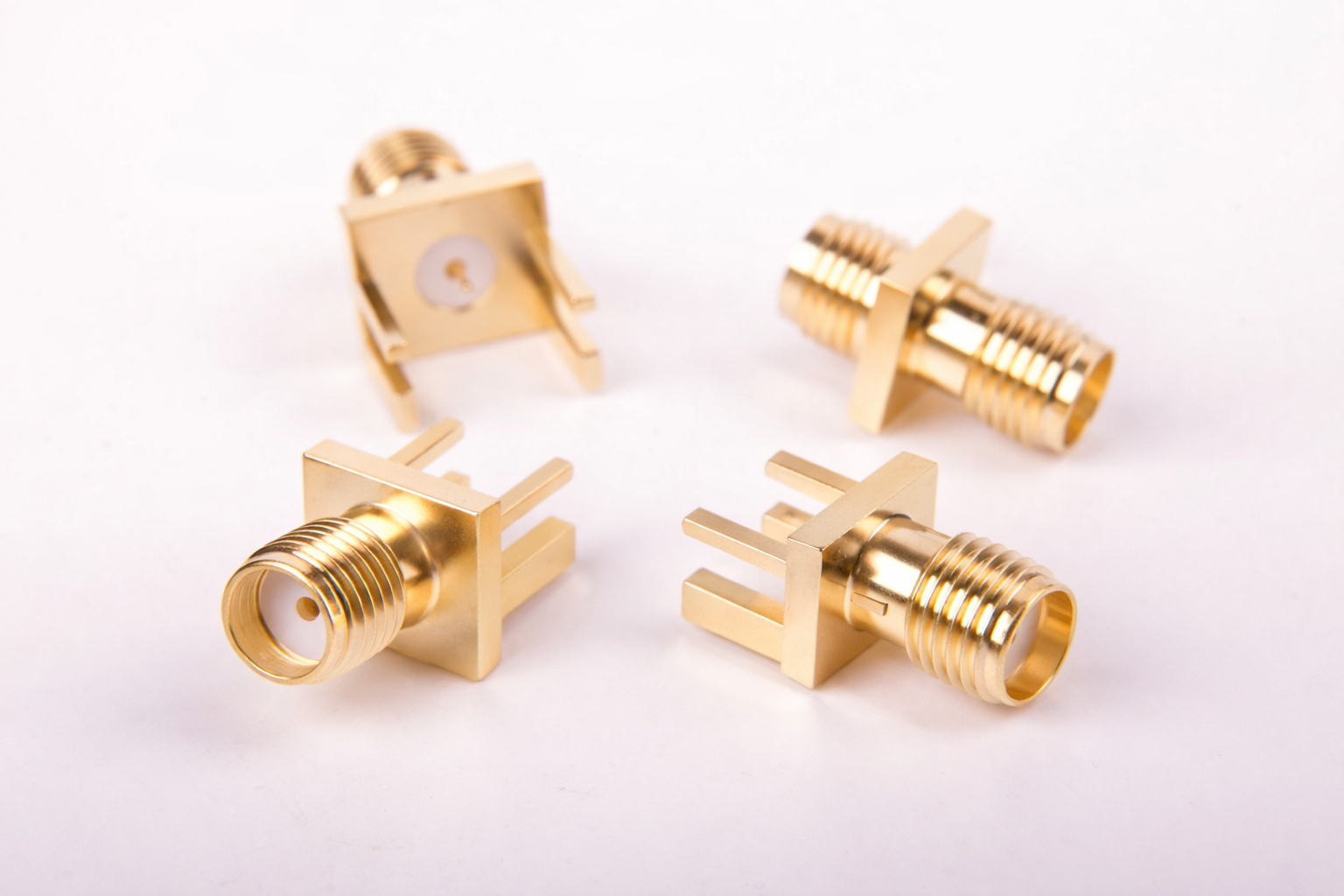
As electronic systems continue to shrink in size while increasing in performance, the demand for reliable, high-frequency interconnect solutions has never been greater. Among the many RF connector types available today, the SMA (Sub-Miniature Type A) موصل stands out as one of the most widely used and trusted solutions. Its ability to deliver stable, low-loss signal transmission in compact form factors has made it indispensable across industries ranging from telecommunications and aerospace to industrial automation and medical technology.
In particular, SMA connectors play a critical role in modern medical devices, where signal integrity, mechanical reliability, and long-term performance are non-negotiable. Whether supporting diagnostic imaging, patient monitoring, or therapeutic equipment, SMA connectors help ensure accurate data transmission and dependable system operation.
What Is an SMA Connector?
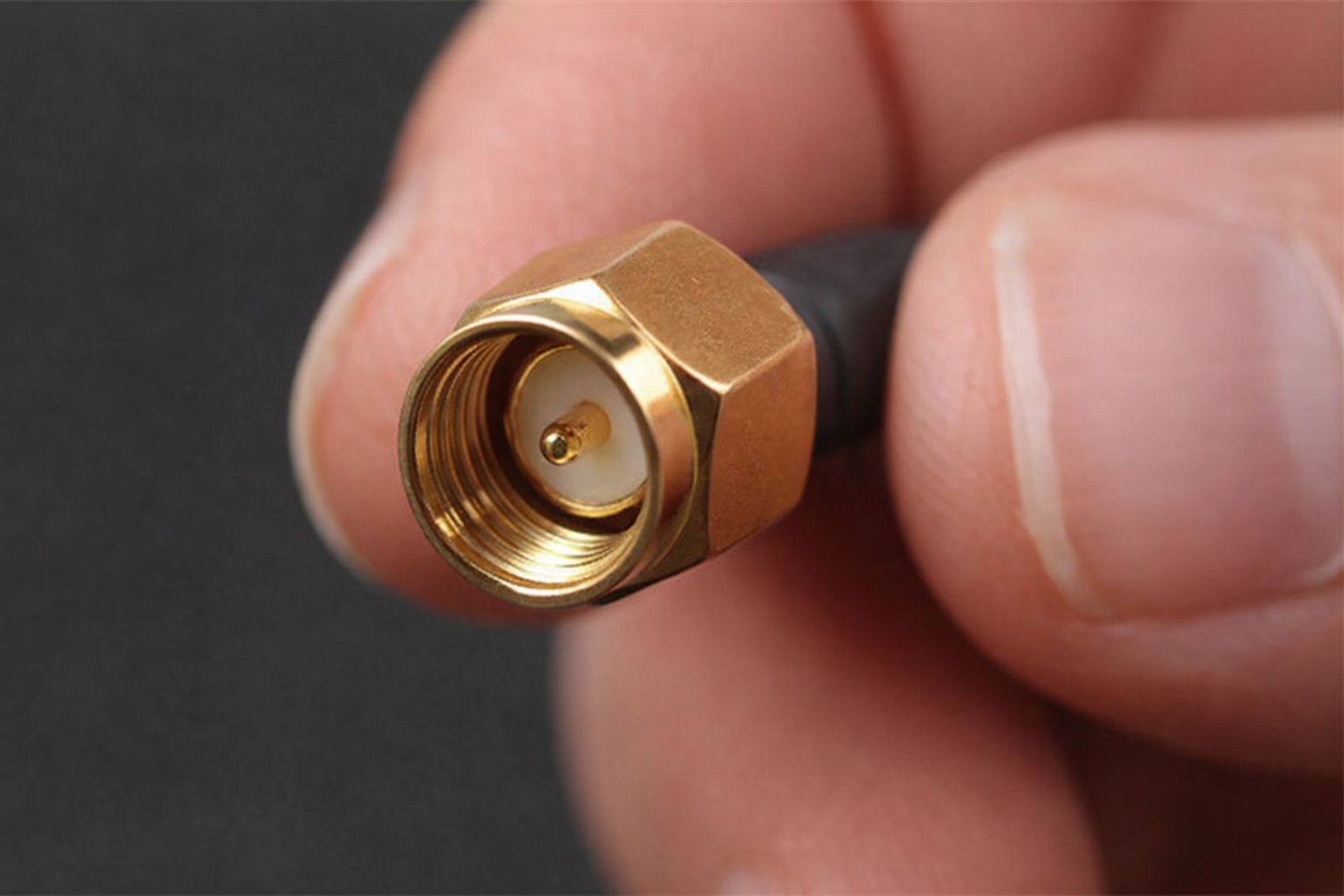
An SMA connector is a coaxial RF connector designed for high-frequency signal transmission in compact electronic systems. The term SMA stands for Sub-Miniature Type A, reflecting its small size compared to earlier RF connectors.
SMA connectors typically operate from DC or the kHz range up to 18 GHz, with some precision variants capable of even higher frequencies. A key feature of the SMA connector is its constant characteristic impedance of 50 ohms, which is the industry standard for RF and microwave systems. Maintaining this impedance minimizes signal reflection and ensures efficient power transfer across the connection.
Electrical and Mechanical Characteristics of SMA Connectors
SMA connectors use a coaxial design, consisting of a central conductor surrounded by a dielectric insulator and an outer conductor. This structure enables excellent shielding and consistent impedance control, which are essential for high-frequency applications.
Mechanically, SMA connectors employ a threaded coupling mechanism, providing a secure, اتصال مقاوم للاهتزاز. Unlike push-on RF connectors, the screw-type interface ensures consistent contact pressure and prevents accidental disconnection, even in demanding environments.
Although SMA connectors resemble standard coaxial connectors, they are not directly compatible with common consumer cable or internet connections. Specialized adapters are required when interfacing SMA connectors with other coaxial systems.
Standard SMA Connector Specifications
Key technical specifications commonly associated with standard SMA connectors include:
¼-36 threaded coupling interface
Male SMA connectors featuring a 5/16-inch hex nut, allowing torque application with a standard ½-inch wrench
Female SMA connectors with a coupling thread length of approximately 4.32 mm
Integrated silicone rubber O-rings that provide environmental sealing against dust and contaminants
Designed for repeated mating cycles while maintaining electrical performance
These standardized dimensions and features enable compatibility across a wide range of RF components and systems.
Types of SMA RF Connectors

SMA connectors are available in both male and female configurations. Male connectors are easily identified by the presence of a center pin inside the threaded outer conductor, while female connectors contain a corresponding socket.
In typical system designs, female SMA connectors are mounted on fixed devices such as circuit boards or enclosures, while male connectors are attached to removable cables. This arrangement offers flexibility for maintenance, upgrades, and system reconfiguration.
Role of SMA RF Connectors in Medical Applications
Medical devices often rely on RF signals for imaging, sensing, and communication. In these applications, even minor signal degradation can affect system accuracy or reliability. SMA RF connectors are widely used in medical equipment because they provide:
Consistent signal integrity at high frequencies
Mechanical robustness for long-term use
Secure connections resistant to vibration and handling
Compact size suitable for space-constrained designs
These attributes make SMA connectors ideal for diagnostic systems, patient monitoring devices, and minimally invasive medical technologies.
Designing SMA RF Connectors for Optimal Performance
Designing an SMA connector for a specific application requires careful attention to geometry, مواد, and assembly techniques. SMA connectors are available in straight-angle and right-angle configurations, allowing designers to optimize signal routing and mechanical layout.
Right-angle designs are particularly popular because they help maintain controlled impedance while saving space. لكن, improper design or assembly can lead to impedance mismatch, which results in signal reflection and performance loss. Common causes include excessive solder, dimensional inaccuracies, air gaps, or mechanical deformation.
Precision engineering and controlled manufacturing processes are essential to prevent these issues.
Mounting Options for SMA Connectors
SMA connectors are offered in several mounting styles to accommodate different system requirements:
Panel Mount: Suitable for rugged industrial and military environments
Bulkhead Mount: Allows secure attachment through panels using nuts and washers
Through-Hole Mount: Available in vertical or right-angle orientations, including non-magnetic versions for medical use
Edge Mount: Designed for PCB edge installation, available in standard and drop-in styles
Each mounting option is selected based on mechanical stability, space constraints, and environmental exposure.
Reliability and Signal Integrity Considerations
In mission-critical systems, signal loss or intermittent connections are unacceptable. SMA connectors are designed to maintain consistent electrical contact and shielding throughout their service life. Proper torque application, اختيار المواد, and environmental protection are all essential to preserving long-term reliability.
Importance of UL Certification for SMA RF Connectors
UL certification plays a crucial role in ensuring safety and reliability, particularly in medical and industrial applications. UL-certified SMA components have been tested for structural integrity, متانة, and electrical performance under defined operating conditions.
Using certified components allows engineers to design systems with predictable behavior and reduced risk, especially where regulatory compliance is required.
Quality Management and Manufacturing Standards
High-performance SMA connectors are the result of rigorous quality management systems. ايزو 9001:2015 certification ensures that every stage of production—from design and sourcing to assembly and inspection—follows documented, repeatable processes.
This process-driven approach minimizes variability and ensures consistent product quality.
Impedance Matching and System Integration
Impedance matching is critical in RF systems, and SMA connectors must work seamlessly with cables, terminations, and other components. Poor matching leads to reflection, signal loss, and potential system instability.
Successful integration requires a system-level approach, where connectors are selected and tested as part of the complete RF pathway.
Testing and Validation of SMA RF Connectors
Before reaching full-scale production, SMA connectors undergo extensive prototyping and testing. This includes:
Environmental stress testing (temperature extremes, humidity, salt exposure)
Mechanical durability testing
RF performance measurements using automated test equipment
Custom test fixtures for unique or specialized designs
These validation steps ensure that connectors perform reliably under real-world conditions.
Developing Custom SMA RF Connector Solutions
Custom SMA connector projects begin with a thorough understanding of application requirements, including frequency range, mechanical constraints, and environmental exposure. Collaboration between design, engineering, and manufacturing teams ensures that each solution meets performance, cost, and timeline objectives.
خاتمة: Delivering Reliable SMA RF Connectivity
The SMA connector remains one of the most versatile and dependable RF interconnect solutions available today. Its combination of compact size, high-frequency capability, القوة الميكانيكية, and design flexibility makes it suitable for a wide range of demanding applications.
From advanced medical devices to industrial and telecommunications systems, SMA connectors continue to deliver reliable performance where precision and signal integrity matter most. By focusing on thoughtful design, rigorous testing, and high manufacturing standards, engineers can ensure that SMA connectors perform flawlessly throughout the life of the system. اتصل بنا for more information.
الأسئلة الشائعة
1. What limits the maximum operating frequency of standard SMA connectors?
The frequency limit of standard SMA connectors (typically up to 18 GHz) is determined by dimensional tolerances, dielectric material properties, and connector interface geometry. At higher frequencies, even microscopic deviations in conductor alignment or dielectric spacing can cause impedance discontinuities, increased return loss, and signal degradation.
2. How does torque affect SMA connector performance?
Proper torque is critical for SMA connectors. Under-torquing can lead to poor electrical contact and increased insertion loss, while over-torquing can deform the connector interface, damage the dielectric, or misalign the center conductor. Most SMA connectors require a tightening torque of 8–12 in-lb (0.9–1.35 N·m) for optimal performance and longevity.
3. What causes SMA connector wear over repeated mating cycles?
Repeated mating can cause wear on the center contact and coupling threads, particularly if connectors are mated at improper angles or without torque control. Gold-plated contacts help minimize wear and maintain low contact resistance. Precision SMA connectors are typically rated for 500 or more mating cycles when properly handled.
4. How do SMA connectors perform in high-vibration environments?
SMA connectors perform well in vibration-prone environments due to their threaded coupling mechanism. لكن, in extreme vibration or shock conditions, secondary retention methods such as thread-locking compounds or safety wire may be used to prevent loosening while preserving electrical performance.
5. What is the difference between standard SMA and precision SMA connectors?
Precision SMA connectors feature tighter dimensional tolerances, higher-quality materials, and improved surface finishes. These enhancements allow precision SMA connectors to support higher frequencies (often beyond 18 GHz), improved return loss, and greater repeatability, making them suitable for laboratory, test, and metrology applications.
6. Can SMA connectors be used for DC and low-frequency signals?
نعم. SMA connectors can transmit DC and low-frequency signals in addition to RF and microwave signals. Their coaxial structure ensures stable electrical performance across a wide frequency spectrum, making them suitable for mixed-signal applications where both RF and DC power are required.
7. How do environmental factors affect SMA connector reliability?
Exposure to moisture, temperature extremes, and corrosive atmospheres can impact SMA connectors over time. Environmental sealing features such as O-rings, corrosion-resistant plating, and appropriate material selection are critical for maintaining performance in harsh environments, especially in medical, البحرية, والتطبيقات الصناعية.
8. What design considerations are critical when integrating SMA connectors into PCB layouts?
Key considerations include controlled impedance trace design, proper ground stitching, minimal transition discontinuities, and accurate connector placement. Edge-mount and through-hole SMA connectors require precise PCB pad geometry to prevent impedance mismatch and signal reflection at high frequencies.


