When it comes to electrical systems, whether at home, in the car, or in industrial settings, the proper use of wire connectors is crucial for safety, efficiency, and long-lasting performance. Wire connectors, also known as electrical connectors or terminals, are essential components that ensure secure connections between wires or other electrical components. This article will provide an in-depth look at the various types of wire connectors, their applications, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
Introduction to Wire Connectors
Wire connectors are devices used to join two or more electrical conductors together. They are commonly used to connect wires in a circuit, ensuring that electricity flows correctly from one part of a system to another. By securely joining wires, connectors help to avoid potential electrical faults, including loose connections, short circuits, and fire hazards.
Electrical wire connectors come in different shapes, sizes, and materials, each designed for specific applications. The right choice of connector is essential for safety, functionality, and ease of maintenance.
Overview of Different Types of Wire Connectors
Twist-on Wire Connectors
Twist-on wire connectors, often referred to as wire nuts, are among the most commonly used connectors. These connectors are typically plastic caps that twist onto the exposed ends of two or more wires. The twist action ensures a secure connection, and the plastic housing helps to insulate the wires from contact with each other or external elements.

- Common Uses: Residential wiring, lighting circuits, and low-voltage applications.
- Advantages: Easy to install, cost-effective, and versatile. These connectors work with a variety of wire sizes and are available in different colors to indicate compatibility with specific wire gauges.
Crimp Connectors
Crimp connectors include a range of connector types, such as butt connectors, spade connectors, et ring terminals. These connectors rely on a crimping tool to squeeze the connector around the wire, creating a secure and permanent electrical connection. Crimping ensures a strong, reliable connection that will not easily loosen.

- Common Uses: Automotive wiring, appliance connections, industrial machines, and high-performance circuits.
- Advantages: Crimp connectors provide a strong, secure connection that is resistant to vibration and can withstand extreme temperatures.
Solderless Connectors
Solderless connectors, as the name suggests, do not require soldering for secure connections. These connectors are designed to fit over the wire and are often used in DIY projects, appliances, or situations where quick, reliable connections are necessary without the need for a soldering iron.

- Common Uses: Household wiring, small electrical appliances, and temporary connections.
- Advantages: Fast and easy to use, these connectors eliminate the need for specialized tools like a soldering iron.
Push-In Wire Connectors
Push-in wire connectors are becoming more popular due to their ease of use. These connectors have spring-loaded grips inside that automatically secure the wire once it’s pushed into the connector. They are especially useful for quick, tool-free installations.

- Common Uses: Low-voltage circuits, home electrical wiring, and quick connection needs.
- Advantages: Tool-less installation, reliable connection, and ease of use in tight spaces.
Pin, Spade, Ring, and Fork Terminals
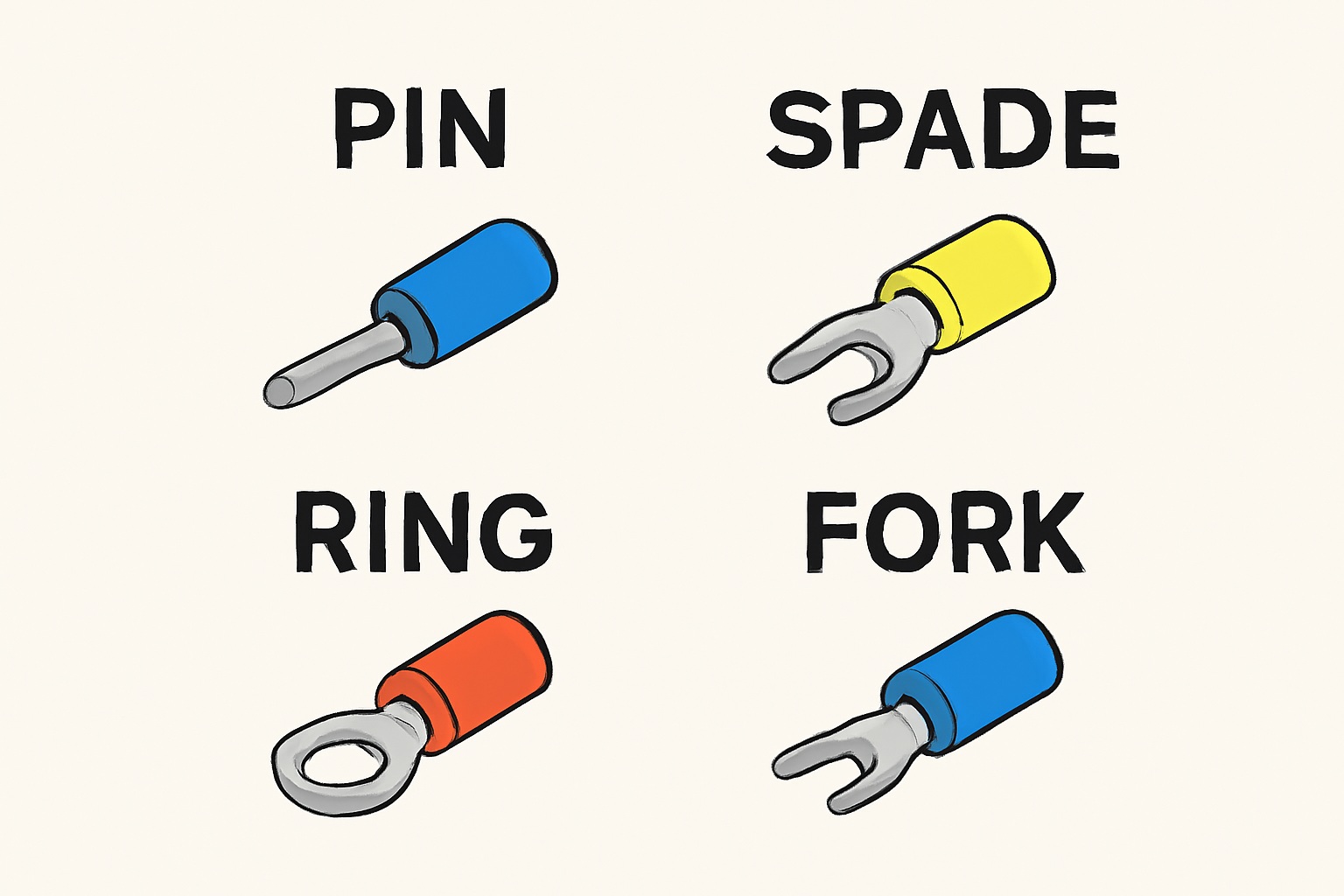
- Pin Connectors: These feature a pin that fits into a corresponding socket or terminal block. Commonly used in audio equipment, computers, et electronics.
- Spade Connectors: Flat connectors with a tab that fits into a terminal screw or bolt. Frequently used in automobileet industrial applications.
- Ring Terminals: These round connectors have a hole in the center, which can be fastened to a screw or bolt. Ring terminals are often used in electrical panelsor grounding systems.
- Fork Terminals: U-shaped connectors that slide over terminal screws for a secure connection. Common in machineryet electrical systems.
- Advantages: These connectors offer secure, reliable connections that can be easily installed or removed as needed.
Heat Shrink Connectors

Heat shrink connectors are designed to offer additional insulation and protection. These connectors come with a heat-shrinkable tubing that tightens around the wire once heated, providing a water- and dust-proof seal. They are ideal for outdoor and harsh environments.
- Common Uses: Automobile, marine, and industrial applications where the environment may expose the connection to moisture or high temperatures.
- Advantages: Extra protection against moisture, corrosion, and environmental damage.
Applications and Best Use Cases for Different Connectors
Residential Wiring
For most home electrical projects, twist-on wire connectors are often the go-to option. These connectors are easy to use, and their versatility allows them to be used in a variety of wiring applications, from light fixtures to outlets. Push-in wire connectors are also popular for quick connections in low-voltage systems such as smart home devices.
Automotive Wiring
In automotive applications, butt connectors, ring terminals, et spade connectors are commonly used. Butt connectors are ideal for connecting two wires end-to-end, while spade and ring terminals allow for secure connections to terminal blocks or screws.
Industrial and Commercial Applications
For industrial systems, where the electrical environment is more demanding, crimp connectors such as fork terminals et ring terminals are preferred. These connectors provide a strong, durable connection that can withstand high vibrations and fluctuating temperatures. Heat shrink connectors are particularly important in harsh environments where moisture protection is essential.
Outdoor and Marine Applications
In environments exposed to moisture, such as boats or outdoor electrical systems, heat shrink connectors are the best choice. Their ability to seal out water and provide extra insulation ensures long-lasting, reliable connections in challenging conditions.
DIY and Low-Voltage Projects
For low-voltage circuits, such as those used in garden lights or security systems, push-in wire connectors et solderless connectors are popular. They offer fast, easy, and safe connections for non-professionals working on small electrical projects.
How to Choose the Right Wire Connector
Choosing the right wire connector for your project is essential to ensure safety, functionality, and durability. Below are key factors to consider:
Matching Connectors to Wire Gauge
The first step is selecting a connector that matches the wire gauge (thickness) you are using. Using the wrong connector can result in a loose connection or damage to the wire. Most wire connectors are color-coded to indicate compatibility with specific wire sizes.
Selecting Connectors Based on Environment
Consider the environment where the connection will be made. If the wires will be exposed to moisture, high heat, or extreme conditions, heat shrink connectors offer superior protection. For connections in dry, controlled environments, standard twist-on connectors may suffice.
Connection Type (Crimp, Twist, Push-In)
For permanent, durable connections, crimp connectors are typically the best option. For temporary or easily removable connections, push-in connectors or twist-on connectors may be more suitable.
Voltage and Current Ratings
Ensure that the connector you choose can handle the voltage and current demands of your system. Check the product specifications to confirm that the connector is rated for the intended electrical load.
Crimping Tools and Installation
What Are Crimping Tools?
Crimping tools are used to securely attach connectors to wires. These tools squeeze the connector around the wire, forming a tight, reliable connection. Crimping tools come in manual, automatic, and hydraulic versions, depending on the scale of the project.
How to Properly Crimp Connectors
To crimp connectors correctly:
- Select the correct size connector for your wire gauge.
- Insert the wire into the connector.
- Use a crimping tool to press the connector around the wire.
- Ensure the connector is tightly secured to avoid any loose connections.
Choosing the Right Crimping Tool
Select a crimping tool that is compatible with the type of connector you are using. For smaller projects, manual crimpers may be sufficient, while larger projects may require hydraulic or ratchet tools.
Advantages of Proper Wire Connector Usage
Safety and Reliability
Using the correct wire connectors ensures that electrical connections are safe, reducing the risk of accidents such as short circuits, electrical fires, or electrocution. Proper connectors also minimize the risk of poor electrical flow, which can lead to malfunctioning devices or equipment.
Durability
High-quality connectors provide long-lasting, durable connections. Choosing the right connector for your environment ensures that your electrical systems will remain stable and functional over time.
Ease of Maintenance
Wire connectors simplify the process of troubleshooting and repairing electrical systems. By using connectors that allow for easy disconnection, repairs can be made quickly without needing to cut and rewire the entire system.
Conclusion
Wire connectors play an essential role in the safety, efficiency, and longevity of electrical systems. From simple residential wiring to complex industrial circuits, choosing the right connector for your needs is crucial. By understanding the various types of connectors, their applications, and how to select the correct one, you can ensure that your electrical projects are both safe and reliable.
FAQ
What is the purpose of a wire connector?
Wire connectors are used to securely join two or more electrical conductors together. They ensure electricity flows correctly, prevent loose connections, short circuits, and fire hazards, and ensure the reliability of electrical systems.
What are the most common types of wire connectors?
The most common types include twist-on wire connectors (wire nuts), crimp connectors, solderless connectors, push-in wire connectors, and various terminal types like pin, spade, ring, and fork terminals.
How do I choose the right wire connector for my project?
To select the appropriate wire connector, consider the wire gauge, environmental conditions (humidité, heat, etc.), connection type (permanent or temporary), and the voltage/current rating needed for the system.
Can I use a crimp connector without a crimping tool?
It is not recommended. Crimping tools ensure a secure and reliable connection. Without the correct crimping tool, the connector may not be tightly secured, leading to poor performance or failure.
What are heat shrink connectors, and when should I use them?
Heat shrink connectors provide additional insulation and protection. When heated, the tubing around the connector shrinks to form a tight, water-resistant seal. They are ideal for use in outdoor, marine, or industrial environments where moisture and harsh conditions are common.
How do I properly use a crimping tool?
To use a crimping tool correctly, select the right connector for your wire, insert the wire into the connector, and use the crimping tool to press the connector firmly around the wire. Ensure the connection is tight to avoid any loose contacts.


