Electrical terminals are used in almost every electrical system you encounter—from automotive wiring harnesses and industrial control panels to household appliances and power distribution equipment. Yet many engineers, buyers, and project managers still underestimate their importance.
In this guide, we explain what electrical terminals are used for, how they function within electrical systems, where they are commonly applied, and how to choose the right terminal for reliable and safe connections.
What Is an Electrical Terminal?
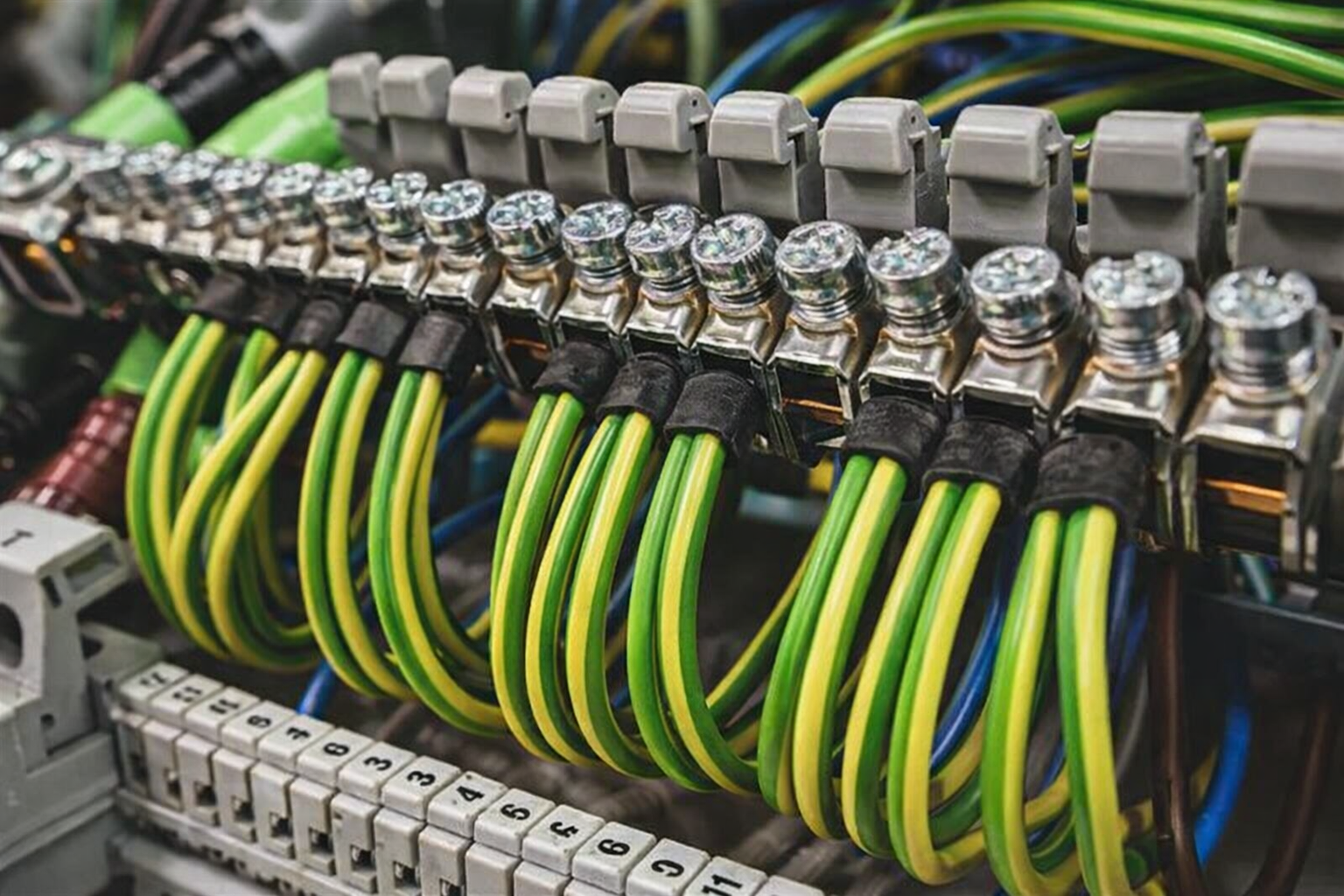
An electrical terminal is the end point of a wire or cable that allows it to connect securely to another electrical component, such as a screw, stud, connector, or terminal block.
In simple terms, terminals ensure that electric current or signals can flow safely and consistently between wires and devices. Without terminals, electrical connections would be unreliable, unsafe, and difficult to maintain.
Unlike connectors (which often join multiple components), terminals are typically used to terminate individual wires in a controlled and secure way.
Core Functions of Terminals in Electrical Systems
Electrical terminals serve several critical functions that directly affect system performance and safety:
1. Electrical Conduction
Terminals provide a low-resistance contact point that allows current or signals to flow efficiently without overheating or power loss.
2. Mechanical Security
They hold wires firmly in place, preventing loosening caused by vibration, beweging, of thermische uitzetting.
3. Circuit Protection and Stability
Properly selected terminals reduce the risk of arcing, short circuits, and connection failure over time.
4. Easy Installation and Maintenance
Terminals allow wires to be installed, removed, or replaced without damaging the conductor, making maintenance faster and safer.
Where Are Electrical Terminals Used?
Real-World Applications
Electrical terminals are used across almost every industry that relies on electrical power or signal transmission.
Automotive Electrical Systems
Terminals are widely used in wiring harnesses, ECUs, sensoren, relais, and battery connections, where vibration resistance and long-term reliability are critical.
Industrial Control Panels and Automation
In control cabinets and PLC systems, terminals ensure organized wiring, easy troubleshooting, and compliance with safety standards.
Power Distribution and Energy Systems
Ring and lug terminals are commonly used in power supplies, switchgear, inverters, and energy storage systems to handle high current loads.
Consumer Electronics and Home Appliances
Compact terminals enable secure connections in appliances, lighting systems, HVAC equipment, and consumer devices.
Aerospace and Medical Equipment
High-reliability terminals are used where failure is not an option, requiring strict material control, precision, and certification.
Common Types of Electrical Terminals and Their Uses
Different terminal types are designed for different connection methods and environments.
Ring Terminals
Designed to fit over studs or screws, ring terminals provide excellent resistance to vibration and are commonly used in automotive and industrial applications.
Spade (Fork) Terminals
These terminals allow quick installation and removal without fully removing the screw, making them ideal for maintenance-friendly systems.
Butt Terminals (Butt Splices)
Used to connect two wires end-to-end, butt terminals are common in wiring repairs and harness assemblies.
Bullet Terminals
Consisting of male and female components, bullet terminals allow fast disconnection and reconnection, especially in modular wiring systems.
Flag and Quick Disconnect Terminals
Used in tight spaces, these terminals allow connections at right angles and simplify assembly in compact designs.
How to Choose the Right Terminal for Your Application
Selecting the correct terminal is essential for system reliability. Key factors include:
Wire Size (AWG)
The terminal must match the wire gauge to ensure proper crimping and electrical contact.
Current and Voltage Rating
Using an underrated terminal can lead to overheating, voltage drop, or failure.
Environmental Conditions
Consider temperature, moisture, chemicals, and vibration when choosing terminal materials and insulation.
Insulated vs. Non-Insulated
Insulated terminals provide added safety and protection against short circuits
Non-insulated terminals are cost-effective and commonly used inside protected enclosures
Compliance and Certifications
Many applications require terminals that meet UL, CSA, RoHS, or automotive standards.
Common Mistakes When Using Electrical Terminals
Even high-quality terminals can fail if used incorrectly. Common mistakes include:
Using the wrong terminal size for the wire
Poor crimping techniques
Ignoring environmental exposure
Mixing incompatible materials that cause corrosion
Choosing cost over compliance in regulated industries
Avoiding these mistakes significantly improves system lifespan and safety.
Why Work With a Professional Terminal Manufacturer?
A reliable terminal manufacturer does more than supply parts. They provide:
Consistent material and dimensional quality
Engineering support for terminal selection
Custom terminal solutions for special applications
Compliance with international standards
Stable supply for mass production
For projects where reliability, safety, and long-term performance matter, professional manufacturing support makes a measurable difference.
Veelgestelde vragens
- What is the main purpose of an electrical terminal?
An electrical terminal provides a secure point to connect a wire to another component, ensuring safe and reliable current or signal transmission. - Are terminals and connectors the same thing?
Nee. Terminals typically terminate individual wires, while connectors usually join multiple wires or components together. - Why do terminals fail in electrical systems?
Failures are usually caused by incorrect sizing, poor crimping, environmental exposure, or using terminals not rated for the application. - Do insulated terminals improve safety?
Ja. Insulated terminals reduce the risk of short circuits and accidental contact, especially in exposed or high-density wiring. - Can I use the same terminal for different applications?
Not always. Terminal selection depends on wire size, current, environment, and mechanical requirements. - Are custom terminals necessary?
Custom terminals are often required when standard sizes or shapes cannot meet performance, space, or compliance needs.
Final Note
Understanding what terminals are used for in electrical systems is essential for building safe, efficient, and durable products. Whether you are designing a wiring harness, assembling control panels, or sourcing components for mass production, choosing the right terminal is a small decision that has a major impact.


